Table Of Contents
What Is Over-Invoicing?
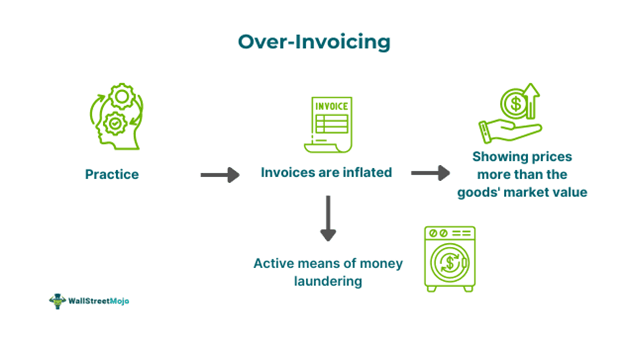
Over-invoicing is a form of masking goods' value, whereby invoices for goods are shared with prices above their market value. This process is often considered an active form of money laundering, in which the people who purchase the goods and services from providers end up paying more than what they should be paying otherwise.
These actions manipulate the value of goods and services in the markets across international borders. Overvaluation allows importers to make it look like they are paying more for imports even when they are not actually doing so. It is a standard method of unethical money movement out or into offshore regions.
Key Takeaways
- Over-invoicing is the practice of showing invoices with inflated prices, i.e., prices higher than the market value of goods and services.
- They result in buyers/importers paying higher amounts to sellers/ exporters, who may then use the money for unethical purposes, such as laundering money, tax evasion, and financial fraud.
- It undermines the financial position and financial integrity and leads to the manipulation of cash flows.
- The practice has vast negative impacts, including a reduction in government revenue, stock market volatility, and large insurance payouts.
Over-Invoicing Explained
Over-invoicing is the practice of inflating the invoice value of goods and services for buyers or importers. In the export industry, the exporter submits an inflated value on the invoice to the importer, which results in a greater transfer value from an importer to an exporter.
The funds obtained through the practice can help in illegal activities, like tax evasion and fraud. Small and medium-sized enterprises can indulge in such practices to inflate their expenses and reduce their taxable income. Again, this is an ethically discouraged practice that can attract penalties if known or reported. Such practice leads to inaccuracies, and hence, financial integrity becomes questionable.
The practice is part of many financial frauds as it can manipulate cash flows besides providing a picture of false financial positions, facilitating illicit activities, etc. They can indicate money laundering, capital fighting, tax evasion, customs and duty evasion, loan fraud, credit manipulation, and many other unethical activities. They can also be causes for kickbacks and corruption, misuse of export incentives, transfer price manipulation, falsification of financial statements, and inflated insurance claims.
Often, both the exporters and importers are involved. However, this manipulation leads to diminishing trust and reduced client loyalty, affecting the business's credibility.
Examples
Let us look at some instances below to understand the over-pricing meaning better:
Example #1
Imagine Ace Ltd. is a US furniture manufacturing company that exports furniture to international retailers. They have been showing good sales for the year as they continue over-invoicing the buyers. Suppose a piece of furniture was valued at a market price of $50,000. They would invoice it at an inflated rate of $75,000, claiming that the wood is of higher quality.
As a result, the furniture maker earns an additional $25,000 in profit. The company realizes that it has to pay more taxes with more income. Thus, to evade taxes, it records increased packaging, shipping, and storage expenses to make up for this extra $25,000.
However, some secret sources reported this unethical practice conducted by Ace Ltd. to the internal revenue department. This complaint held the manufacturer accountable for asking for the falsified value of goods and services. As the charges were found true, the company had to pay significant penalties.
Example #2
In August 2024, the Federal Board of Revenue of Pakistan reported over-invoicing of imports of solar panels. According to reports, two big companies were involved in the imports of solar panels worth ₹72 billion, and the actual sales were at ₹45 billion. It was found that the companies involved had no physical existence, and they transferred approximately ₹20 billion out of the country.
Impact
Given below are some of the impacts that are resulting from the practice:
- It can result in money laundering that can drain an economy.
- The practice can result in a capital fight, with funds being paid to an entity's foreign account, draining its foreign exchange reserves.
- It reduces taxable income and allows businesses to evade taxes by showing increased expenditure, resulting in reduced government income.
- It helps in showing inflated financial positions by reflecting assets or high receivables that can be used to secure loans.
- It leads to corruption.
- Companies use the method to gain subsidies and incentives. This increases the government's financial burden.
- Falsification of financial statements can inflate a company's stock prices and impact the volatility of the stock market.
- It can result in larger insurance payouts than the actual loss incurred, which can cause insurance companies to lose money.
Over-Invoicing vs Under-Invoicing
Both over and under-invoicing involve masking the actual value of the goods and services in question. However, the approach adopted for doing so differs. The differences between both the concepts are given as follows:
Concept
- Over-invoicing refers to the practice of inflating the actual price of goods.
- Under-invoicing, on the other hand, is the opposite, as it refers to the practice of pricing goods less than their actual price.
Essence
- In invoices that are overvalued, the seller/exporter receives more money than the actual value of sold goods.
- Under-invoicing occurs when the buyer/importer receives more money from the sale of goods in the local market. This happens because they have bought the goods at a lesser value from a seller/exporter.
Impact
- In an overvalued invoice, the seller receives value from the buyer.
- In under-invoicing, the seller transfers value to the buyer.

