Table Of Contents
Account Balance Meaning
Account Balance is the balance present in the person's financial repository, like a saving account or checking account at a given point in time. Further, it can also mean the total amount of money that a borrower can pay to a third party, such as a utility company, credit card company and mortgage banker, or another similar lender or creditor.

However, in either of the cases, it represents the net amount after all debit and credit transactions have been factored in. Nevertheless, there are times when an account balance differs from the actual bank account balance in an individual's account owing to some pending transactions or unprocessed cheques at the bank.
Table of contents
- Account balance refers to the balance in a person's financial repository, such as a savings or checking account, at a specific period.
- It can also encompass the overall amount a borrower may pay to a third party, such as a utility company, credit card company, mortgage banker, lender, or creditor, representing their financial obligations.
- Other account balance terms include savings account, current account, and credit card, each with its associated balance.
- Monitoring account balances online, via an app, phone, ATM, etc., helps the account holder to stay informed about their available funds.
Account Balance Explained
The account balance reflects the amount available in an individual or an organization’s repository for the current account period. These balances are carried forward on a monthly basis based on the subtractions of debit and credit entries in the account.
It is a common appearance with bank accounts when a customer does their account balance check, it is found that the balance in the account and available balance to withdraw or transact is different. In such cases, it signifies that there are outstanding payments that are due such as a cheque waiting to be cleared by the clearing house.
Sometimes the total balance of the account is also displayed for the perusal of the customer to give them an idea of their inflows and outflows of cash.
It is also important to keep in mind that most banks expect a minimum amount to be in the individual or a company’s repository at all times. Failing to maintain the minimum balance often leads to extra charges or penalties.
Examples
Let us understand the concept of bank account balance in depth with the help of a few examples. These examples would give us a practical viewpoint to understand the concept.
Example #1
Let us take an example of a credit card. Let us assume that David has made several purchases of $500, $150, and $225, and then returned one of the items that cost him $200.
As mentioned in the previous section, an account balance will include the purchases he made and the item he returned.
Now, Debit balance for David = Expense for purchase of items = $500 + $150 + $225
- Debit balance for David = $875
Again, the Credit balance for David = Cost of items returned
- Credit balance for David = $200
Finally, the Account balance for David = Debit balance – Credit balance
- = $875 - $200 = $675
Example #2
Let us take an example of a current account with a starting balance of $1,500 and try to illustrate the impact of a pending transaction. The account holder recently received a cheque for $2,500, and then he also wrote a cheque for a scheduled automatic payment of $2,000. However, the cheque for the automatic payment is yet to be processed. Determine the account balance and the true balance (fund available for withdrawal).
Since the second cheque is yet to be processed, at this point,
Account balance = Opening balance + Cheque received
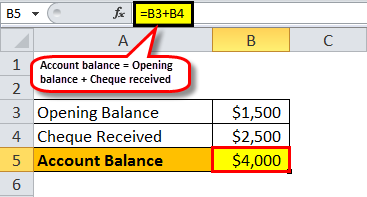
- = $1,500 + $2,500
- = $4,000
However, owing to the unprocessed cheque, the fund available for withdrawal at this point,
True account balance = Opening balance + Cheque received – Cheque written.
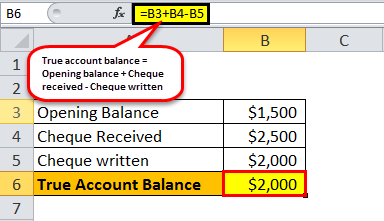
- = $1,500 + $2,500 - $2,000
- = $2,000
It is important to note that although the account balance shows $4,000, the true balance available for withdrawal is $2,000. As such, the account holder should be conscious of the same and record every credit and debit transaction to keep track of the most accurate picture of the account.
Example #3
The Federal Reserve conducted a survey to find out the average bank account balance of citizens of the United States. It was found that the median account balance was $5,300 in 2019.
Despite the fact that different individuals would have a different range that is deposited in the bank based on their income, expenditure, lifestyle, etc, it is advised to keep 15% of pre-tax income aside for savings.
However, a negligible percentage of the U.S. population has a balance that could help them sustain themselves if their income source was abruptly stopped due to losing the job or due to situations such as the pandemic.
It was also found that only 4 in 10 individuals were able to tend to an unexpected expense of $1,000 as there weren’t sufficient funds in their bank accounts.
How To Check?
Conducting an account balance check is not only important but also a necessity in times when cyber fraud and cyber hacking are on the rise.
The account holder is advised to check the funds in their accounts to ensure they maintain their minimum balance, to track their income and spending, and also to ensure no unnecessary charges are levied.
The check can be done through a physical check by visiting the nearest branch of the account and checking the balance through an ATM machine. However, in the modern day it has become easier to check the balance through the bank’s website and mobile application that can deliver the information at a click of a button from the comfort of the customers’ homes.
Relevance and Uses
Despite the differences in needs, income streams, and lifestyles of consumers, understand the relevance and uses of this concept is an important metric with regard to financial planning and most often the first step towards financial independence. It is important to understand the underlying need for an account balance check, and a few of the major points have been listed below:
- The primary requirement is to make sure that the account holder knows how much money is there in the account. It can be checked online, with an app, by phone, at an ATM, etc.
- It is also helpful in keeping track of various bank transactions to ensure that the bank has not overcharged any of the fees or lost any money.
- It also helps match one's records with the bank's records and check if any reconciliation is required.
- Further, regular checking of the balance helps avoid any erroneous transactions and make sure that mistakes are caught before it is too late.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The minimum account balance refers to the lowest amount of money that must be maintained in an account to avoid incurring fees or penalties as per the terms and conditions set by the bank or financial institution.
Account balance refers to the total amount of money in an account at a specific point in time, including all deposits, withdrawals, and other transactions. Available balance, on the other hand, refers to the amount of money that is immediately accessible or usable for transactions, taking into consideration any holds, pending transactions, or restrictions.
Account and statement balances are similar in representing the total amount of money in an account. However, statement balance refers to the balance reflected on a bank statement, typically generated at the end of a billing cycle or a specific period. Therefore, it may not always reflect the most up-to-date or current balance due to recent transactions or pending items. On the other hand, the account balance can be obtained in real-time from the bank or financial institution and may include the most recent transactions and pending items.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Account Balance and its meaning. Here we explain how to check Account Balance, examples, relevance, and uses of the concept. You can learn more about accounting with the following articles –

