Table Of Contents
What Is Profit Formula?
The profit formula in accounting calculates the net gains or losses incurred by the company for any given period by subtracting total expenses from total sales. Profit is the key indicator of the performance of any company.
Profit is considered the key component of operating margin, earnings per share, profitability ratios, etc. There are various statutory guidelines and local GAAPs that all corporations must follow while calculating the profits for any given period. It ensures transparency and allows better comparability in the company’s results.
Key Takeaways
- The profit formula in accounting calculates the net gains or losses of a company for a specific period by subtracting total expenses from total sales.
- Profit is a crucial performance indicator for a company.
- Profit is a key component of various financial metrics such as operating margin, earnings per share, and profitability ratios.
- The profit formula is integral to the income statement as it serves as the foundation for assessing the company's operational performance.
Profit Formula Explained
The profit formula in economics plays a major role in any income statement, as this will form the base to determine the operational matrix of the company.
Profit is the walkthrough through which any non-professionals can understand how the company has arrived at a Profit After Tax (PAT), Profit Before Tax (PBT), Earnings Before Interest Tax Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA).
Formula
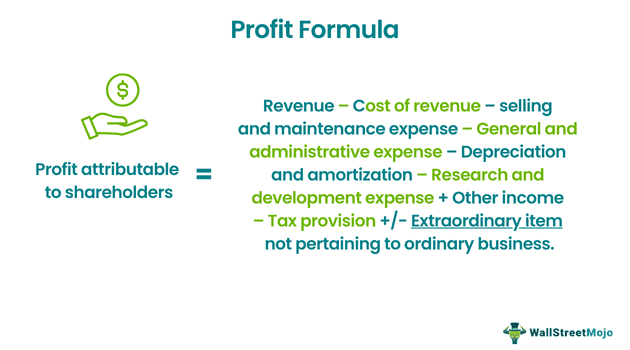
The formula for profit in accounting is:-
Profit Attributable to Shareholders = Revenue – Cost of Revenue – Selling and Maintenance Expense – General and Administrative Expense – Depreciation and Amortization – Research and Development Expense + Other Income – Tax Provision +/- Extraordinary Item not About Ordinary Business.
Thus, the profit formula in economics mentioned above is used to calculate the profit of a business.
How To Calculate?
Below is a detailed explanation of the steps of accounting profit formula: -
- Determine the company's total revenue from the core business activity.
- Then, from revenue, deduct the total cost of revenue incurred for earning the company’s gross revenue. That will help arrive at gross profit and gross margin. The cost of revenue includes salary cost, finance expense, cost of inventory, and such expenses directly related to the business.
- From gross profit, deduct the below expense: -
a. Selling and maintenance expense
b. Depreciation and amortization
c. Research and development expenses.
d. It will give the operating income of the company - For operating income, add other incomes like interest, profit on the sale of the investment, etc., to arrive at a profit before taxes.
- From profit before tax, deduct tax provision for the given period. It will provide profit after tax.
- Every business will have a few unwanted gains or losses incurred during the financial year, which are not ordinary, like the debtor’s bankruptcy, winning/losing any legal suit, etc. Adjust such extraordinary items to profit after tax, which will provide income attributable to shareholders.
Thus, the above are the steps followed while calculating profit using the accounting profit formula.
Examples
Let us see some simple to advanced examples of the profit equation to understand it better.
Example#1
Below are the various incomes and expenses of Microsoft Inc, calculated profit attributable to the shareholders using the total profit formula: -
| Particulars | Amount ( in $) |
|---|---|
| Salary and Wages | 322 |
| Interest Expense | 669 |
| Interest Income | 219 |
| Cost of Inventory | 43,410 |
| Sales Promotion Expense | 1,144 |
| Professional Fees | 1,200 |
| Fees | 452 |
| Dividend Income | 122 |
| Depreciation | 306 |
| Revenue from Sale of IT Products | 57,190 |
Solution:
As per the given profit equation, operating income can be derived as follows: -

Operating Income = 12,789 – 1,144 – 1,200 – 452 - 306
Operating Income = 9,687
Calculation of profit income attributable to shareholders can be done as follows: -

Income Attributable to Shareholders = 9,687 + 122 + 219
Income Attributable to Shareholders = 10,028

Thus, Microsoft Inc. has earned a profit from operating income of $9,687 million for the given period and $10,028 million of profit attributable to shareholders.
Example #2
Let us look at another example to where the using the total profit formula has been used.
Below are the particulars of Alphabet Inc., for the financial year: -
| Particulars | Amount ( in $) |
|---|---|
| Salary and Wages | 403 |
| Interest Expense | 838 |
| Interest Income | 274 |
| Cost of Inventory | 54,436 |
| Sales Promotion Expense | 1,434 |
| Professional Fees | 1,504 |
| Legal Fees | 566 |
| Dividend Income | 152 |
| Depreciation | 383 |
| Revenue from Sale of IT Products | 71,716 |
| Provision for Doubtful Debt | 4,012 |
| Rent Expense | 4,162 |
| Insurance Expense | 1,918 |
| Subscription Expense | 403 |
| Travel Expense | 1,691 |
| Staff Welfare Expense | 420 |
Bifurcate the expense under different heads and calculate the profit attributable to shareholders.
Solution:
As per the given profit formula, operating income can be derived as follows: -

Operating Income = 15,619 – 1,434 – 1,918 – 403 – 1,691 – 1,504 – 566 – 4,012 – 4,162 – 383
Operating Income = - 454
Calculation of profit loss attributable to shareholders can be done as follows: -

Loss Attributable to Shareholders = - 454 + 274 + 152
Loss Attributable to Shareholders = - 28

Explanation
All the expenses are bifurcated into various heads based on their nature. While bifurcating the expense, one must consider whether the expense is directly related to operations. If it is directly related to operations, it will form part of the cost of revenue. Otherwise, it will form part of selling and maintenance, general and administrative expenses, etc., which are considered below-the-line expenses.
Thus, Alphabet Inc. has incurred a loss from operations of $454 million for the given period and a loss of $28 million for the given financial year.
Example #3
Below are the particulars of Apple Inc., for the financial year: -
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
|---|---|
| Wages | 488 |
| Interest Expense | 1,015 |
| Insurance Claim Lodged and Accepted | 111 |
| Communication | 387 |
| Interest Income Expense | 332 |
| Cost of Inventory | 65,983 |
| Employee Stock Obligation Expense | 100 |
| Bank OD Interest Expense | 87 |
| Sales Incentive Expense | 1,738 |
| Audit Fees | 1,823 |
| Court Fees | 686 |
| Bank Guarantee Expense | 63 |
| Brokerage Expense | 22 |
| Dividend Income | 184 |
| Depreciation and Amortization | 464 |
| Revenue from Operations | 86,928 |
| Provision for Insolvency of Debtor | 1,863 |
| Office Rent Expense | 5,044 |
| Insurance Expense | 2,324 |
| Subscription Expense | 488 |
| Commutation Expense | 2,049 |
| Staff Welfare Expense | 509 |
Bifurcate the expense under different heads and calculate the profit attributable to shareholders.
Solution:
As per the given formula, operating income can be derived as follows: -

Operating Income = 17,832 – 1,738 – 2,324 – 2,049 – 1,823 – 686 – 22 – 5,044 – 488
Operating Income = 3,658.
Calculation of profit income attributable to shareholders can be done as follows: -

Income Attributable to Shareholders = 3,631 + 111 – 1,863
Income Attributable to Shareholders = 1,879

Explanation
All the expenses are bifurcated into various heads based on their nature. While bifurcating the expense, one has to keep in mind whether the expense is directly related to operations or not. If it is directly related to operations, it will form part of the cost of revenue. Otherwise, it will form part of selling and maintenance, general and administrative expenses, etc., considered the line expense.
Thus, Apple Inc. has earned profit from operations of $3,658 million for the given period and $1,879 million for the given financial year.
Relevance And Uses
Determining the correct business profit formula is of utmost importance as:
- Profit is considered a key indicator of operating margin.
- Profit is regarded as one of the key measuring areas in competitor analysis.
- Borrowings are sanctioned based on the operating profitability of the company.
- The profit helps in determining the foreseeable future of the company.
- Profit is important to make strategic decisions like continuing the business line or diversifying or divesting the business segment.
Profit Formula Vs Revenue
- The business profit formula is revenue minus cost, whereas the revenue formula is total sales multiplied by the price per unit.
- Revenue is the total income the business generates and profit is the revenue remaining after all expenses have been paid.
- It is possible for a business to earn good revenue but still may not be profitable due to high amount of expenses.
- We view the revenue on the top of income statement whereas the profit is found at the end of the income statement.

