Table of Contents
What Are The Accounting Assumptions?
Accounting assumptions refers to a set of rules that ensures the business operations of an organization are conducted efficiently and as per the standards defined by the FASB (Financial Accounting Standards Board). These assumptions, in addition to accounting principles and concepts, become guidelines for any business firm letting them operate in order.
It ultimately helps in laying the groundwork for consistent, reliable, and valuable information and it is based entirely on the fundamentals like accrual, consistency, reliability and objectivity, monetary unit assumption, business entity assumption, period, going concern, historical costs, full disclosures, and conservatism.
Accounting Assumptions Explained
Accounting assumptions define the mechanism for reporting financial transactions in the financial statements. These are rules that make it mandatory for the companies to conduct their business operations and reporting mechanism as per the standards laid out by the FASB. The purpose of accounting assumptions is to provide a basis of consistency that the readers of the financial statements can use to evaluate the genuineness of a company's financials and confirm its financial well-being depicted in the same.
These are fundamental to the well-being of an organization. These assumptions lay the groundwork for how a financial transaction must be reported in the financial statements and make it mandatory for the companies to ensure complete adherence to all the statutory requirements.
It highlights the reliability, authenticity, and reliability of an organization’s financial statements. These are beneficial for the company, its management, and the readers of the financial statements.
Fundamental List
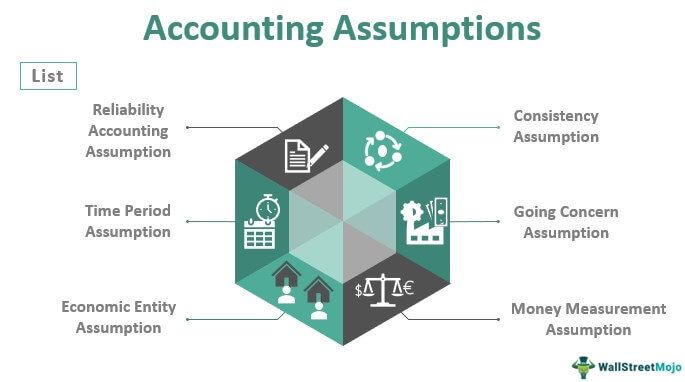
The basic accounting assumptions that enable businesses to operate in a proper manner include the following:
#1 - The Reliability Assumption
This assumption makes it mandatory for the companies to record only such accounting transactions that can be easily proven. In other words, financial transactions that can be verified through invoices, billing statements, receipts, and bank statements must only be recorded in the financial statements.
#2 - The Consistency Assumption
This assumption makes it substantial for the companies to use a consistent method of accounting for all the accounting periods. Having a consistent method of accounting will ensure an easy comparison between the company's financial statements for different financial periods.
#3 - The Time Period Assumption
This assumption states that the accounting practices and methods used by an entity must be reported and maintained for a particular period. The companies must ensure that these periods remain consistent for each year. It becomes easy for the readers of the financial statements to compare the same for different periods. This assumption is also known as periodic or accounting period assumption.
#4 - The Going Concern Assumption
Going Concern is also termed a continuity assumption. Per this assumption, a company will continue to deliver its business operations and continue to exist for an unforeseeable future. This assumption is based on the fact that a company will never go bankrupt, and it shall be able to perform its business operations for a more extended period.
#5 - The Economic Entity Assumption
This assumption separates the owner of the company from the company itself. It means that the economic entity assumption separates the company's financial records from that of the personal financial records of the company's owner. In all probabilities, the commercial business transactions must not mix with the individual transactions of the company’s owner. This assumption is also known as the business entity assumption.
#6 - The Money Measurement Assumption
Money Measurement concept states that every worth transaction recording must be recorded and expressed in monetary terms. The money measurement assumption enhances the understanding of a business concern's financial state of affairs.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the accounting assumptions definition better:
Example #1
Suppose there are two firms operating in the market. While firm A takes up loans and has debt obligations, which it takes seriously and pays off the amount from time to time, firm B, which has almost similar financial liabilities is hardly bothered about paying off its debt, despite having enough ways to pay off the outstanding dues. In such a scenario, the lack of seriousness is reflected in the case of the latter, which ultimately raises doubts in the minds of the stakeholders.
This is one of the assumptions, namely, the Going Concern assumption, which, based on the activities of firms A and B reveals that the former is interested in continuing to operate, while firm B has some other plans and may not be willing to continue to operate.
Example #2
The United States Financial Accounting Standard Board or FASB, given the rising popularity and willingness of people to invest in cryptocurrencies, has approved rules for accounting to ensure the platforms have an idea about the accounting assumptions and principles for better operation in the crypto market. According to the reports, these are expected to be effective in 2025.
This is an important step taken in the financial sector as crypto is becoming one of the most widely used financial instruments.
Importance
Accounting assumptions may not be accurate all the time, but they are the fundamental guidelines to help businesses understand the basic standard based on which they should operate. The importance of these assumptions, however, have been listed below. Let us have a look:
- These assumptions are huge for the organization, its management, and the readers of the financial statements. It helps establish a robust framework for reliable and consistent information.
- It enhances the reliability, verifiability, and objectivity of financial statements. The purpose of such assumptions is to enable the users of the financial statements to evaluate and confirm the genuineness of an organization's financial records and assess economic well-being. There is no doubt that these assumptions help in the establishment of credibility.
- It offers a systematic structure concerning how the accounting transactions of an organization for a particular financial period must be recorded and reported in the financial statements. The analyst and potential and existing investors can verify the accuracy, reliability, authenticity, and comparability of the financial statements for different accounting periods with the help of accounting assumptions.
- The users of the financial statements can even make significant investment-related decisions based on the genuineness, reliability, and financial results depicted in a company's financial statements. It enables the management to make necessary decisions based on the results of the financial statements. It helps minimize or eliminate the presence of potential errors and frauds in the same.
Benefits
The benefits of accounting assumptions are reaped not just by the companies and their management but also by the investors. These benefits are as follows-
- These are beneficial for all kinds of investors, whether they are potential or existing ones. The investors can assess the genuineness of the company's financial statements and accordingly determine the true and fair view of a company's financial well-being. It enables the investors to make crucial investment-related decisions based on their reasoning. It saves them from being manipulated by false representations of the transactions in a company's financial statements.
- These are beneficial for the management of an organization too. The management of an entity gets to know its actual well-being, and based on these results, the former can make appropriate decisions and ensure that the latter does better the next time.
- It helps the companies attain their long-term and short-term business goals and objectives.

